关键字
以下是Java中的关键字列表,按照功能分类:
| 分类 | 关键字 |
|---|---|
| 访问控制 | private, protected, public |
| 类、方法和变量 | class, interface, enum, extends, implements, new, this, super, instanceof |
| 数据类型 | byte, short, int, long, float, double, char, boolean, void |
| 流程控制 | if, else, switch, case, default, while, do, for, break, continue, return |
| 异常处理 | try, catch, finally, throw, throws |
| 修饰符 | abstract, final, static, synchronized, transient, volatile, native, strictfp |
| 包相关 | package, import |
| 其他 | assert, const (未使用), goto (未使用) |
说明:
const和goto是Java保留的关键字,但目前并未使用。strictfp用于确保浮点运算的跨平台一致性。transient用于标记不需要序列化的字段。volatile用于标记可能被多个线程同时访问的变量。
这些关键字在Java中具有特殊含义,不能用作标识符(如变量名、类名等)。
static
the static keyword in java is mainly used for memory management.The static keyword in java is used to share the same variable or method of a given class.
The users can apply static keyword with variables,methods,blocks,and nested(嵌套的) classes.
The static keyword belongs to the class than an instance of the class.
The static keyword is used for a constant(n 常量 adj 不变的) variable or a method that is the same for every instance of a class
For
- variable
- blocks
- methods
- classes
member
when a member is declared static,it can be accessed before any objects of its class are created
and without reference to any object
class Test
{
static void m1(){
"from m1".sout
}
main{
m1();
}
}static block
if you need to do the computation in order to initialize your static variables,you can declare a static block that gets executed(执行 实施) exactly once, when the class is first loaded
class Test{
static int a = 10;
static int b;
static{
"static block initialized".sout
b = a* 4;
}
main{
a.sout;
b.sout;
}
}static variable
当将变量声明为静态时,则在类级别的所有对象之间创建并共享该变量的单个副本。 静态变量基本上是**(((本质的)全局变量。类的所有实例共享相同的静态变量。
important points for static variables:
- we can create static variables at the class level only
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fun());
}
static int fun(){
static int x = 10; //Error static local variable are not allow
return x--;
}
}In java, a static variable is a class variable(for whole calss) so if we have static
local(局部的 当地的 本地的) variable(a variable with scope limited to function) it violates(违反 违背) the purpose of static. hence compiled does not allow static local variable.
- static block and static variables are executed in the order they are present in a program
public class Test2 {
static int a = m1();
static {
System.out.println("inside static block");
}
static int m1(){
System.out.println("from m1");
return 20;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("from main");
System.out.println(a);
}
}static methods
当用静态关键字声明方法时,它是 konwn 作为静态方法。静态方法的最常见示例是 main()方法。
如上所述,可以在创建其类的任何对象并且不参考任何对象之前访问任何静态成员。被声明为静态的方法具有 Servel 限制:
- 他们只能直接调用其他静态方法
- 他们只能直接访问静态数据
- 静态方法是属于类的,而不是类的某个特定对象实例。因此,在静态方法的执行过程中,没有 this 引用,这意味着它们无法直接访问实例变量或实例方法
- 静态成员(包括静态变量和静态方法)在类被加载到 JVM 时就已经存在,而不需要创建类的任何对象实例。这就意味着静态方法可以在没有任何对象实例存在的情况下被调用。如果静态方法被允许访问非静态成员,那么在没有实例化对象的情况下,这些非静态成员根本就不存在,从而可能导致运行时错误
- They cannot refer to this or super in any way
package Static;
public class Test4 {
static int a = 10;
int b =10;
void m2(){
System.out.println("from m2");
}
static void m1(){
a = 20;
System.out.println("from m1");
// b = 20; cannot make a static reference to the non-static field;
// m2(); cannot make a static reference to the non-static method m2()
// System.out.println(super.a);
}
}static classes
只有当它是嵌套类(内类)时,才能使一个类成为静态
我们无法用静态修饰符声明顶级类,但可以将嵌套类声明为静态类。类型的类称为嵌套静态类。固定的静态类不需要外部类的引用。 在这种情况下((案例)(案例)(案例)**),静态类无法访问外部类的非静态成员。
Java 允许在另一个类中定义类。这些类别称为嵌套的 Calsses。类别可以是静态的, 作为内部类; 如果没有外部类的实例,就无法创建内部类的实例,因此内部类实例可以访问其外部类的所有成员,而无需使用对外部类实例的参考。出于此原因,内部类可以 帮助使程序简单简洁; 可以在不实例化外部类的情况下实例化静态嵌套类。
package Static;
public class StaticNestedClass {
private static String str = "this is jasper";
static class NestedClass{
public void disp(){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NestedClass nestedClass = new NestedClass();
nestedClass.disp();
}
}初始化顺序
静态变量和静态语句块优先于实例变量和普通语句块,静态变量和静态语句块的初始化顺序取决于它们在代码中的顺序。 存在继承的情况下,初始化顺序为:
- 加载父类的静态内容:首先加载并初始化父类的静态变量和静态代码块,静态内容只在类首次加载到 JVM 时初始化一次。
- 加载子类的静态内容:接着加载并初始化子类的静态变量和静态代码块,同样,这些静态内容只初始化一次。
- 初始化父类的实例变量和普通语句块:当通过构造函数创建对象的实例时,首先初始化父类的实例变量和普通(非静态)初始化块。
- 执行父类的构造函数:执行父类的构造函数,完成父类的构建。
- 初始化子类的实例变量和普通语句块:然后初始化子类的实例变量和普通初始化块。
- 执行子类的构造函数:最后,执行子类的构造函数,完成子类对象的创建。
when to use static variavble and methods
为所有对象共有的属性使用静态变量。例如,在班级学生中,所有学生共享相同的大学名称,使用静态方法来更改静态变量;
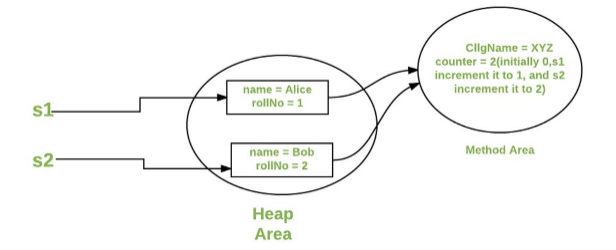
package Static;
public class Student {
String name;
int id;
static String collegeName;
static int counter = 0;
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.id=setid();
}
static int setid(){
counter++;
return counter;
}
static void setCollegeName(String name){
collegeName = name;
}
void getStudentInfo(){
System.out.println("name:" + this.name);
System.out.println("id:" + this.id);
System.out.println("collegeName:" + collegeName);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student.setCollegeName("xupt");
Student jasper = new Student("jasper");
Student cliff = new Student("cliff");
jasper.getStudentInfo();
cliff.getStudentInfo();
}
}
Q&A
short s1 = 1; s1 = s1 + 1;有错吗?short s1 = 1; s1 += 1;有错吗 对于 short s1 = 1; s1 = s1 + 1;由于 1 是 int 类型,因此 s1+1 运算结果也是 int 型,需要强制转换类型才能赋值给 short 型。 在Java中,所有的整数计算至少会自动提升到 int 类型 而 short s1 = 1; s1 += 1;可以正确编译,因为 s1+= 1;相当于 s1 = (short(s1 + 1);其中有隐含的强制类型转换。 复合赋值运算符会自动进行类型转换
